
If a hyphen ( -) isĪppended to the package name (with no intervening space), the identified package will be removed if it is currently installed. The /etc/apt/ sources.list(5) file is used to locate the repositories for the desired packages. Each package is a package name, not a fully qualified filename (for instance, inĪ Fedora Core system, glibc would be the argument provided, not glibc-2.4.8.i686.rpm).Īll packages required by the package(s) specified for installation will alsoīe retrieved and installed. This option is followed by one or more packages desired for installation. See also apt_preferences(5) for a mechanism for over-riding the general settings for individual packages. The /etc/apt/ sources.list(5) file contains a list of locations from
#Sudo update update#
An update must be performed first so that apt-get knows that new versions ofĭist-upgrade In addition to performing the function of upgrade, this option also intelligently handles changing dependencies with new versions of packages Īpt-get has a "smart" conflict resolution system, and it will attempt to upgrade the most important packages at the expense of less important ones, if
#Sudo update install#
Install status of another package will be left at their current version. New versions of currently installed packages that cannot be upgraded without changing the

Packages that are not already installed retrieved and installed. Packages currently installed with new versions available are retrieved and upgraded under no circumstances are currently installed packages removed, nor are Upgrade Used to install the newest versions of all packages currently installed on the system from the sources enumerated in /etc/apt/ sources.list(5). An update should always be performed before an upgrade or dist-upgrade. The indexes of available packages are fetched from the location(s) specified in Update Used to re-synchronize the package index files from their sources. Sudo apt-get update to update the list of repositories, and then sudo apt-get upgrade to update the system.įrom the terminal itself it is much faster and more comfortable than from the Ubuntu update managerSurely when you learn these simple commands, you will not update your system from that manager again.Unless the -h, or -help option is given, one of the commands below must be present.
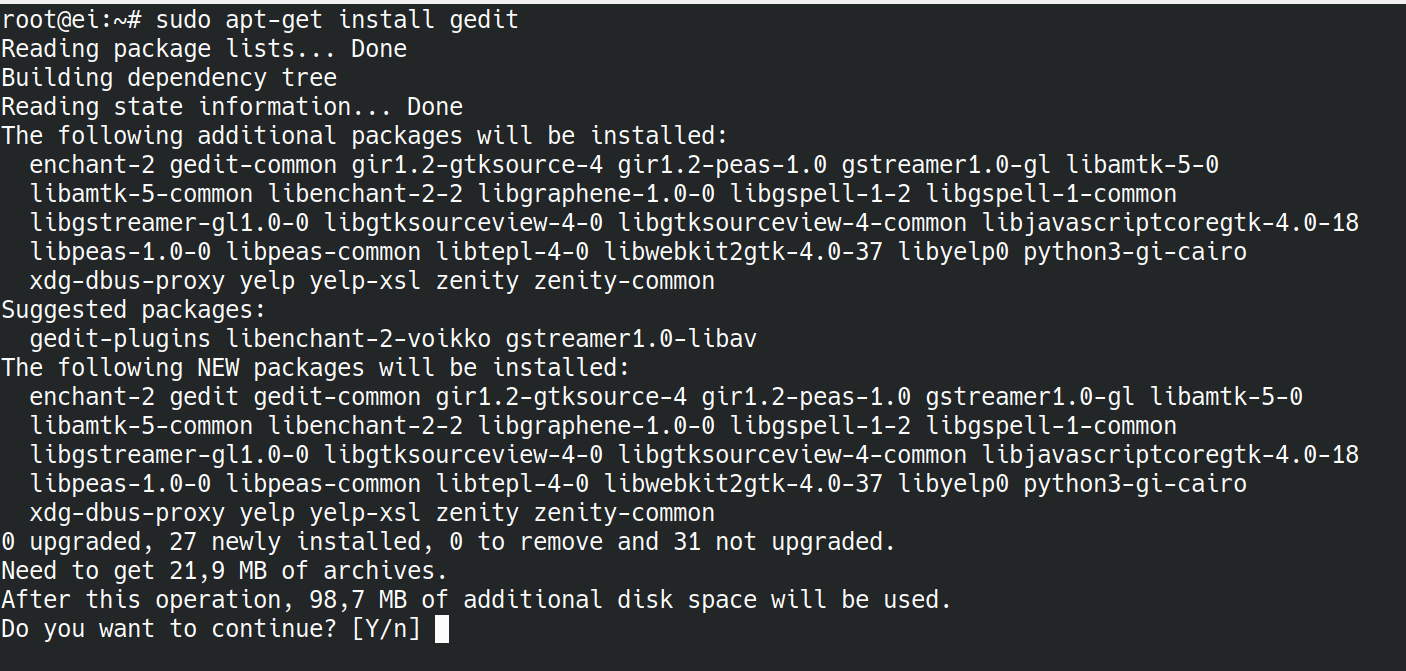
If you want search for updates for your system and install them, you only have to execute the two previous commands from a terminal: The new installed application can be found in the application / graphics menu or typing from the terminal itself gimp to dry. With this we will have installed the new Gimp app in our system, in addition to having updated the list of repositories and our own operating system. Now we would install the program with the following command:īy last we would update our whole system with the following command: With this line we will update the list of repositories installed in our system:
#Sudo update download#
To better understand the process to follow, we are going to carry out a Practical exercise installing us the gimp, which is a program similar to PhotoshopOnly open source or Open Source, which means that it is totally free for those who want to download it.įirst of all, it will be to open a new terminal and run the next line:
#Sudo update how to#
In the following practical tutorial for novice usersI'm going to teach you how to install applications from the terminal itself, as well as how to update the list of repositories and the operating system itself. As I have already told you in other articles, the Linux terminal is the most versatile tool of our operating system, since from it we will control and we can run and install any program of our system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
